Search This Supplers Products:Magnetic materials, magnetic equipment and devicesAuto Partstelecom devicesElectronicselectricalsmetals
Demagnetization
publisherGordon
time2020/10/08
- Demagnetization, also known as magnetic cleaning, demagnetization, etc., refers to the process of magnets returning to a magnetic neutral state, and can also be called magnetic neutralization.
In industrial processing, there are three methods of demagnetization:
1. Static demagnetization
Add a magnetic field that is opposite to the original magnetization direction of the magnet. The strength of this diamagnetic field should ensure that when it is removed, the magnetic induction intensity of the magnetic body becomes zero. The resulting magnetic neutral state is called the static magnetic neutral state.
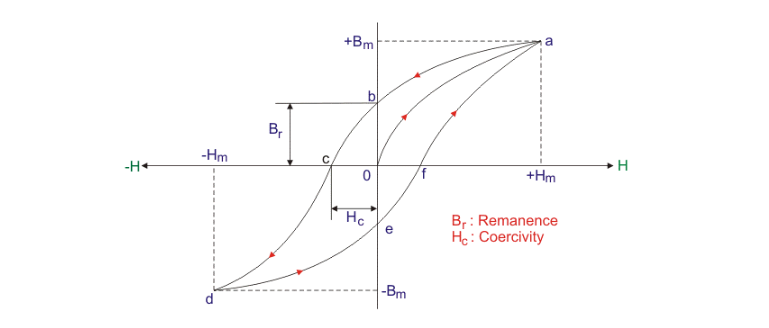
In the hysteresis loop, the demagnetization curve of the second quadrant is that when a magnet is applied with a magnetic field opposite to the magnetizing direction, its magnetic induction intensity decreases with the increase of the reverse magnetization field. When this reverse magnetization When the field strength reaches -Hc, the magnetic induction intensity of the magnet drops to 0, and the magnet no longer has magnetism.
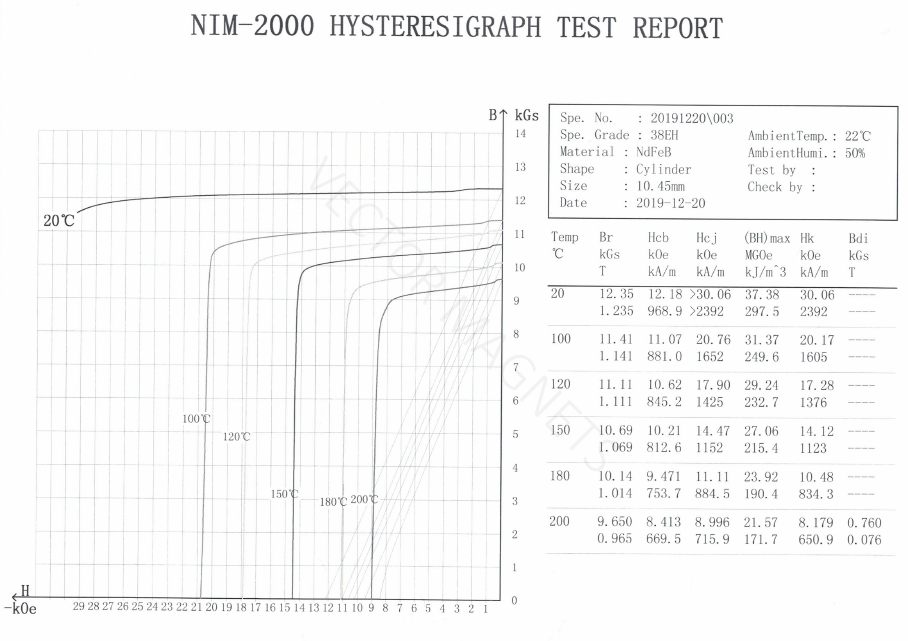
The hysteresis loop is measured at room temperature, and the demagnetization curve of the magnet is not the same at different working temperatures, as shown in the figure below. Therefore, the strength of the reverse magnetic field applied for demagnetization is different under different temperature conditions.
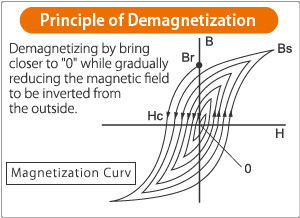
2. Dynamic demagnetization
Apply a sufficiently strong alternating magnetic field to the magnetic body, and then gradually reduce the amplitude of the alternating magnetic field to zero. The resulting magnetic neutral state is called dynamic magnetic neutral state. The working principle is to place the workpiece in an alternating magnetic field and use the hysteresis loop to demagnetize. As the amplitude of the alternating magnetic field gradually decays, the trajectory of the hysteresis loop becomes smaller and smaller. When the magnetic field gradually decays to zero, the residual magnetism in the workpiece will be close to zero. The principle of demagnetization is shown in the figure on the right. The direction and size of the current and magnetic field must be changed at the same time during demagnetization.
3. Thermally induced demagnetization
The magnetic body is heated to above the Curie temperature, and then cooled and demagnetized without the action of an external magnetic field. The resulting magnetic neutral state is called the magnetic neutral state.
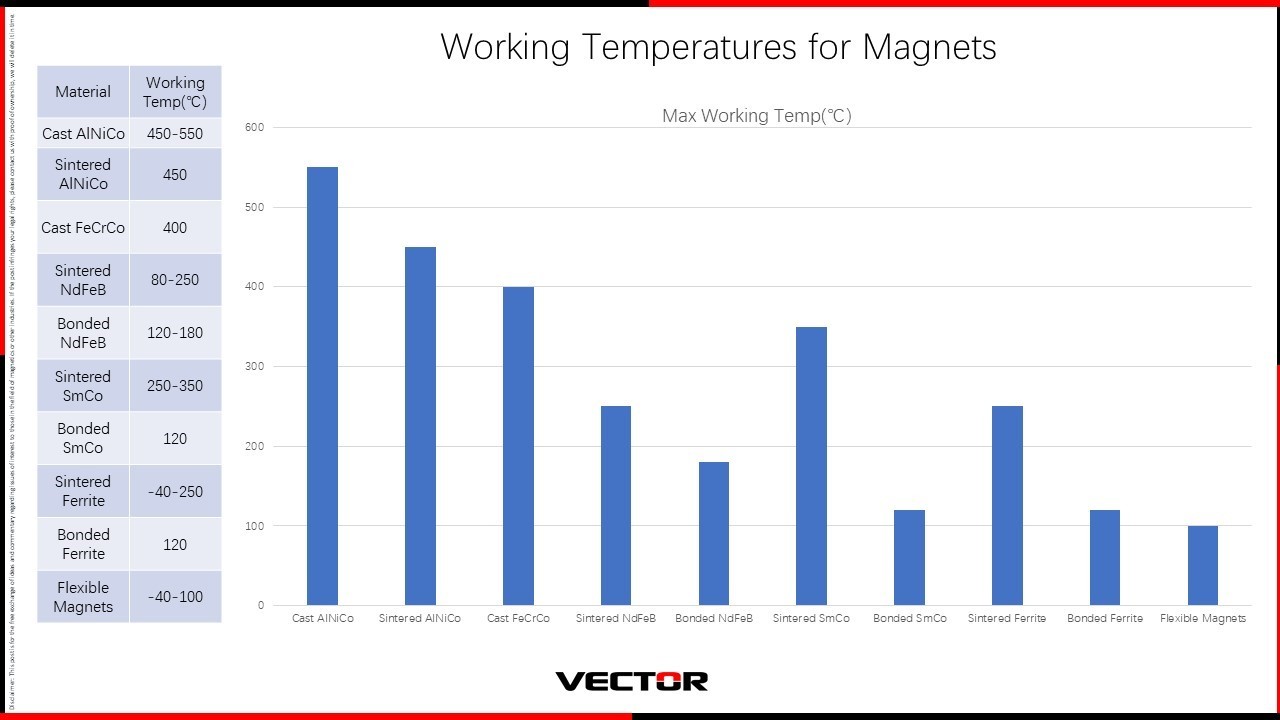
The following is the Curie temperature and maximum working temperature of various magnets.